الوحدة 18 المجالات المغناطيسية
Magnetic fields
القسم 1-18 فهم المغناطيسية
https://youtu.be/zVUthzBv1UA
https://youtu.be/cFlOvd29Bpo
بور بونت الدرس ( جديد)
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1lyWB9L5j5CscVPRH0XrVjJXunR9uWFi3/view?usp=sharing
القسم 2- تطبيقات القوى المغناطيسية
https://youtu.be/wGSNf0HZPYs
بور بونت الدرس ( جديد)
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1ppJ2xc1cEVU3iGuDYOInXbBdQnHmFwAH/view?usp=sharing
اسئلة اختيار من متعدد على المجالات المغناطيسية
https://youtu.be/4o8PF3UgULQ
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B976YZX4SobqT0hLSU14N1cyNHM/view?usp=sharing
اسئلة وأجوبة على المجالات المغناطيسية
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B976YZX4SobqcE05dWxZMmlhODA/view?usp=sharin
قواعد اليد اليمنى
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Xv_4es334VM
اختبار معياري على المجالات المغناطيسية
https://youtu.be/_UIB2Zti3cw
بور بونت انجليزي على المجالات والقوى المغناطيسية
https://youtu.be/cFlOvd29Bpo
بور بونت الدرس ( جديد)
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1lyWB9L5j5CscVPRH0XrVjJXunR9uWFi3/view?usp=sharing
القسم 2- تطبيقات القوى المغناطيسية
https://youtu.be/wGSNf0HZPYs
بور بونت الدرس ( جديد)
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1ppJ2xc1cEVU3iGuDYOInXbBdQnHmFwAH/view?usp=sharing
اسئلة اختيار من متعدد على المجالات المغناطيسية
https://youtu.be/4o8PF3UgULQ
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B976YZX4SobqT0hLSU14N1cyNHM/view?usp=sharing
اسئلة وأجوبة على المجالات المغناطيسية
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B976YZX4SobqcE05dWxZMmlhODA/view?usp=sharin
قواعد اليد اليمنى
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Xv_4es334VM
اختبار معياري على المجالات المغناطيسية
https://youtu.be/_UIB2Zti3cw
بور بونت انجليزي على المجالات والقوى المغناطيسية
بيفيد المتقدم والعام لأنه شامل
https://drive.google.com/file/d/15s5vBVQfvtAu3n9B6XAoy4QgCeo6IHBx/view?usp=sharing
اسئلة القسم 1-18 فهم الفيزياء
اتقان المفاهيم من
1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wASnm70m2ro
اتقان المفاهيم
38-39-40-41-42-43-44-45-46-47-48-49-50-51-58-59-60-61-62-63-64-65-70
اتقان المفاهيم من
1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wASnm70m2ro
اتقان المفاهيم
38-39-40-41-42-43-44-45-46-47-48-49-50-51-58-59-60-61-62-63-64-65-70
1. If you hold a bar magnet in each hand and bring your hands close together, will the force be attractive or repulsive
if the magnets are held in the following ways?
a. the two north poles are brought close together
b. a north pole and a south pole are brought together
SOLUTION:
a. repulsive
b. attractive
2. Figure 4 shows five disk magnets floating above one another. The north pole of the top-most disk faces up. Which
poles are on the top side of each of the other magnets?
SOLUTION:
south, north, south, north
3. The ends of a compass needle are marked N and S. How would you explain to someone why the pole marked N
points north? A complete answer should involve Earth’s magnetic poles.
SOLUTION:
Earth’s geographic north pole is actually its southern magnetic pole.
4. CHALLENGE When students use magnets and compasses, they often touch the magnets to the compasses. Then they find that the compasses point south. Explain why this might occur.
SOLUTION:
When students bring compasses near magnets, the magnetization of the compasses flips. The iron in the compass needle becomes a temporary magnet.
5. How does the strength of a magnetic field that is 1 cm from a current-carrying wire compare with each of the following?
a. the strength of the field 2 cm from the wire
b. the strength of the field 3 cm from the wire
SOLUTION:
a. Because magnetic field strength varies inversely with distance from the wire, the magnetic field at 1
cm will be twice as strong as the magnetic field at 2 cm.
b. Because magnetic field strength varies inversely with distance from the wire, the magnetic field at 1
cm will be three times as strong as the magnetic field at 3 cm.
6. A long, straight current-carrying wire lies in a north-south direction.
a. The north pole of a compass needle placed above this wire points toward the east. In what direction is the current?
b. If a compass were placed underneath this wire, in which direction would the compass needle point?
SOLUTION:
a. from south to north
b. west
7. A student makes a magnet by winding wire around a nail and connecting it to a battery, as in Figure 13. Which
end of the nail—the pointed end or the head—is the north pole?
SOLUTION:
the pointed end
8. You have a battery, a spool of wire, a glass rod, an iron rod, and an aluminum rod. Which rod could you use to make an electromagnet that can pick up steel objects? Explain.
SOLUTION:
Use the iron rod. Iron would be attracted to a permanent magnet and take on properties of a magnet, whereas aluminum or glass would not. This effect would support the magnetic field in the wire coil and thus make the strongest electromagnet.
مسائل الوحدة
19. Explain the method you could use to determine the direction of force on a current-carrying wire at right angles to a magnetic field. Identify what must be known to use this method.
SOLUTION:
You would use the right-hand rule for magnetic force on a wire. When you point the fingers of your right
hand in the direction of the magnetic field and your thumb in the direction of the wire’s conventional
(positive) current, the palm of your hand will face in the direction of the force acting on the wire. To use
this method, you would need to know the direction of the current and the direction of the field.
19-
اشرح الأسلوب الذي يمكنك اتباعه لتحديد اتجاه القوة على سلك يحمل تياراً بزوايا
قائمة على مجال مغناطيسي
. حدد ما يجب أن يكون
معلوماً باستخدام هذا الاسلوب
.
20. A wire that is 0.50 m long and carrying a current of 8.0 A is at right angles to a 0.40-T magnetic field. How strong is the force that acts on the wire?
SOLUTION:
F = ILB = (8.0 A)(0.50 m)(0.40 N/Aim ) = 1.6 N
20-سلك
يبلغ طوله 0.50m ويحمل تيارا شدته 8.0A يتعامد على مجال مغناطيسي شدته 0.40T . ما القوة المغناطيسية
التي تؤثر على السلك
؟
21. A wire that is 75 cm long and carrying a current of 6.0 A is at right angles to a uniform magnetic field. The magnitude of the force acting on the wire is 0.60 N. What is the strength of the magnetic field?
21-
سلك يبلغ طوله 75Cm ويحمل تيارا شدته 6.0A يتعامد على مجال مغناطيسي .مقدار القوة المؤثرة
على السلك 0.60N كم يبلغ قوة المجال المغناطيسي ؟
22. A 40.0-cm-long copper wire carries a current of 6.0 A and weighs 0.35 N. A certain magnetic field is strong enough to balance the force of gravity on the wire. What is the strength of the magnetic field?
22-
سلك نحاسي طوله 40.0Cm يحمل تياراً شدته 6.0A ويزن 0.35N . هناك مجال مغناطيسي
معين قوي مما يكفي لموازنة قوة الجاذبية على السلك . ما
قوة ( شدة)المجال المغناطيسي ؟
23. How much current would be required to produce a force of 0.38 N on a 10.0-cm length of wire at right angles to a 0.49-T field?
23-ما
شدة التيار المطلوب لإنتاج قوة مغناطيسية تبلغ 0.38N على سلك بطول 10.0Cm بزاوية قائمة على مجال مغناطيسي قوته ( شدته) 0.49T ؟
24. CHALLENGE You are making your own loudspeaker. You make a 1-cm-diameter coil with 20 loops of thin wire.
You use hot glue to fasten the coil to an aluminum pie plate. The ends of the wire are connected to a plug that goes into the earphone jack on an MP3 music player. You have a bar magnet to produce a magnetic field. How would you orient the magnetic field to make the plate vibrate and produce sound?
SOLUTION:
One pole should be held as close to the coil as possible so that the field lines are perpendicular to both the wires and the direction of motion of the plate.
25. In what direction is the force on an electron if that electron is moving east through a magnetic field that points north?
26. What are the magnitude and direction of the force acting on the proton shown in Figure 20?
25-
ما اتجاه القوة على إلكترون إذا كان يتحرك إلى الشرق عبر مجال مغناطيسي يشير إلى الشمال ؟
26-
ما مقدار واتجاه القوة المؤثرة على البروتون الظاهر في الشكل 20 ؟
27. A stream of doubly ionized particles (missing two electrons and thus carrying a net charge of two elementary charges) moves at a velocity of 3.0×104 m/s perpendicular to a magnetic field of 9.0×10−2 T. How large is the force acting on each ion?
27 –
تدفق من الجسيمات ثنائية التأين
( تفقد إلكترونين
وبذلك تحمل شحنتين موجبتين أساسيتين
) بسرعة 3.0x104m/s عمودياً على مجال
مغناطيسي يبلغ 9.0x10-2T كم تبلغ القوة
المغناطيسية المؤثرة على كل أيون
؟
28. Triply ionized particles in a beam carry a net positive charge of three elementary charge units. The beam enters a magnetic field of 4.0×10−2 T. The particles have a speed of 9.0×1 m/s and move at right angles to the field. How large is the force acting on each particle
28 –
دخلت حزمة من الجسيمات ثلاثية التأين
( يحمل كل منها ثلاث
شحنات موجبة أساسية ) مجالاً مغناطيسياً
يبلغ 4.0x10-2T تبلغ سرعة الجسيمات 9.0x106m/s وتتحرك عمودياً على
المجال المغناطيسي . ما مقدار القوة
المغناطيسية التي تؤثر على كل جسيم
؟
29. A singly ionized particle experiences a force of 4.1×10−13 N when it travels at right angles through a 0.61-T magnetic field. What is the particle’s velocity?
29 –
يتعرض جسيم أحادي التأين لقوة تبلغ4.1x10-13N عندما يتحرك بزاوية قائمة عبر مجال مغناطيسي يبلغ 0.61T ما سرعة الجسيم ؟
30. CHALLENGE Doubly ionized helium atoms (alpha particles) are traveling at right angles to a magnetic field at a speed of 4.0×104 m/s. The force on each particle is 6.4×10−16 N. What is the magnetic field strength?
30 – التحدي : ذرات هيليوم ثنائية التأين ( جسيمات ألفا) تتحرك
بزوايا قائمة في مجال مغناطيسي بسرعة 4.0x104m/s تبلغ القوة على كل
جسيم 6.4x10-16N ما قوة المجال المغناطيسي ؟
31. MAIN IDEA Explain how electric motors use magnets to convert electrical energy to mechanical energy.
SOLUTION:
An armature in a magnetic field rotates 360° as a split-ring commutator changes the direction of current,
producing mechanical energy.
32. Magnetic Forces Imagine that a current-carrying wire is perpendicular to Earth’s magnetic field and runs eastwest.
If the current is east, in which direction is the force on the wire?
SOLUTION:
up, away from the surface of Earth
33- مسارعات الجسيمات : في مسارع الجسيمات
تعمل المجالات المغناطيسية على تقسيم إشعاعات الجسيمات إلى أجزاء الدائرة .وتعمل المجالات
الكهربائية على زيادة سرعة الإشعاعات
.؟
a-
يدور شعاع البروتونات في اتجاه حركة عقارب الساعة .
ما الاتجاه الذي يجب أن
يأخذه المجال المغناطيسي ؟
وما الاتجاه الذي يجب ان تأخذه المجالات الكهربائية ؟
b-
إذا كان شعاع من الجسيمات سالبة الشحنة سيدور في عكس اتجاه حركة عقارب الساعة . فهل يجب تغيير اتجاه
المجال المغناطيسي ؟ وهل يجب تغيير اتجاه
المجالات الكهربائية ؟
34. Galvanometers Compare the diagram of a galvanometer in the left part of Figure 17 with the electric motor in Figure 19. How is the galvanometer similar to an electric motor? How is it different?
SOLUTION:
Both the galvanometer and the electric motor use a loop of wire positioned between the poles of a permanent magnet. When a current passes through the loop, the magnetic field of th permanent magnet exerts a force on the loop. The loop in a galvanometer cannot rotate more tha 180°. The loop
in an electric motor rotates through many 360° turns. The motor’s split-ring commutator allows the current in the loop to reverse as the loop becomes vertical in the magnetic field, enablin the loop to spin in the magnetic field. The galvanometer measures unknown currents; the electric motor has many uses.
34- الجلفانومتر : قارن مخطط جلفانومتر في الجزء الأيسر من
الشكل 17 مع المحرك الكهربائي
في الشكل 19 . ما وجه الشبه
بينهما؟وما وجه الاختلاف
؟
35. Motors When the plane of an armature in a motor is perpendicular to the magnetic field, the forces do not exert a torque on the coil. Does this mean that the coil does not rotate? Explain.
SOLUTION:
Not necessarily; if the coil is already in rotation, then rotational inertia will carry it past the point of zero torque. It is the coil’s acceleration that is zero, not the velocity.
35. المحركات عندما يكون مسطح الملف الدوار في محرك عمود ً يا على المجال المغناطيسي، لا تفرض القوى عزم دوران على الملف. هل يعني هذا أن الملف لا يدور؟ اشرح ذلك.
35. Motors When the plane of an armature in a motor is perpendicular to the magnetic field, the forces do not exert a
torque on the coil. Does this mean that the coil does not rotate? Explain.
SOLUTION:
Not necessarily; if the coil is already in rotation, then rotational inertia will carry it past the point of zero torque. It is the coil’s acceleration that is zero, not the velocity.
36. المقاومة: يتطلب جلفانوميتر 180 μA لانحراف كامل المدى. عند استخدامه كمقياس جهد كهربائي، ما إجمالي المقاومة المطلوبة (مقاومة الجلفانوميتر ومقدار المقاومة المتصلة) لانحراف كامل المدى بقياس 5.0 V ؟
36. Resistance A galvanometer requires 180 μ A for full-scale deflection. When it is used as a voltmeter, what total resistance of the meter and the multiplier resistor is needed for a 5.0-V full-scale deflection?
SOLUTION:
37. Critical Thinking: Two current-carrying wires move toward each other when they are placed parallel to each other. Compare the directions of the two currents. Explain your reasoning.
SOLUTION:
Because the force is attractive, the currents are in the same direction. That is, an up current in the first wire creates a magnetic field that intersects the second wire. If the current in the second wire is in the same direction, the force on it will pull the wires together.
37- التفكير الناقد : سلكان يحملان تياراً . يتحركان نحو بعضهما
عند وضعهما بالتوازي مع بعضهما
. قارن بين اتجاهي التيارين . اشرح أسبابك .
38. State a rule describing magnetic attraction and repulsion
SOLUTION:
Like poles repel one another; opposite poles attract.
39. Describe how a temporary magnet differs from a permanent magnet.
SOLUTION:
A temporary magnet is like a magnet only while under the influence of another magnet. Its domains will revert to a random arrangement when the magnet is removed. The domains of a permanent magnet are permanently aligned.
40. Name three common ferromagnetic elements.
SOLUTION:
iron, cobalt, and nickel
41. BIG IDEA Draw a small bar magnet with field lines around it. Use arrows to show the direction of the field. Draw a small nail in this magnetic field with the induced north and south poles indicated. The bar magnet's field exerts an attractive force on one pole of the nail and a repulsive force on the other. Why is the nail pulled toward the bar magnet?
The bar magnet's field is stronger closer to the bar magnet, so the attractive force on the closer pole is stronger than the repulsive force on the further pole, making a net attractive force.
42. Draw the magnetic field between two like magnetic poles and then between two unlike magnetic poles. Show the directions of the fields.
43. If you broke a magnet in two, would you have isolated north and south poles? Explain.
SOLUTION:
No; new poles would form on each of the broken ends.
44. Describe how to use a right-hand rule to determine the direction of a magnetic field around a straight, currentcarrying wire.
SOLUTION:
Grasp the wire with your right hand, keeping your thumb pointing in the direction of the conventional current through the wire. Your fingers will encircle the wire and point in the direction of the magnetic field.
45. If a current-carrying wire were bent into a loop, why would the magnetic field inside the loop be stronger than the magnetic field outside?
SOLUTION:
The magnetic field is concentrated inside the loop because the direction of the fields from the individual loops is always the same, and the fields add together.
46. Describe how to use a right-hand rule to determine the north and south ends of an electromagnet.
SOLUTION:
Grasp the electromagnet with your right hand, keeping your fingers encircling the electromagnet in the
direction of the conventional current flow through the loops. The thumb of your right hand will point
toward the north pole of the electromagnet.
47. Each atom in a piece of iron is like a tiny magnet. The iron, however, may not be a magnet. Explain.
SOLUTION:
The poles of the atoms do not necessarily align in the same direction. When not in the presence of a
strong magnet, the iron is not magnetized; the poles of its atoms point in random directions. If the iron
were placed near a strong magnet, however, the poles of the atoms would align.
48. Why will heating a magnet weaken it?
SOLUTION:
Its domains are jostled out of alignment. Chapter Assessment
Section 1 Understanding Magnetism: Mastering Problems
49. Refer to Figure 22 to answer the following questions. (Level 1)
a. Where are the poles?
b. Where is the north pole?
c. Where is the south pole?
SOLUTION:
a. 4 and 2, by definition
b. 2, by definition and field direction
c. 4, by definition and field direction
Move to the right. Unlike poles attract.
52. Figure 25 shows the response of a compass in two different positions near a magnet. Where is the south pole of the magnet located? (Level 1)
SOLUTION:
At the right end. Unlike poles attract.
66. A wire that is 0.50 m long and carrying a current of 8.0 A is at right angles to a uniform magnetic field. The force on the wire is 0.40 N. What is the strength of the magnetic field? (Level 1
66-
سلك يبلغ طوله 0.50m ويحمل تياراً شدته 8.0A يتعامد على مجال
مغناطيسي منتظم . تبلغ القوة على السلك
0.40N كم تبلغ قوة( شدة)
المجال المغناطيسي ؟
67. A wire that is 25 cm long is at right angles to a 0.30-T uniform magnetic field. The current through the wire is 6.0 A. What is the magnitude of the force on the wire? (Level 1
67-
سلك يبلغ طوله 25cm يتعامد على مجال
مغناطيسي 0.30T . يبلغ التيار المار
عبر السلك 6.0A ما مقدار القوة على السلك ؟
68. A wire that is 35 cm long is parallel to a 0.53-T uniform magnetic field. The current through the wire is 4.5 A. What force acts on the wire?
SOLUTION:
If the wire is parallel to the field, no force is produced.
69. The force acting on a wire that is at right angles to a 0.80-T magnetic field is 3.6 N. The current in the wire is 7.5 A. How long is the wire? (Level 1)
68-
سلك يبلغ طوله 35cm يوازي مجالاً
مغناطيسياً منتظم بقياس 0.35T يبلغ التيار المار
عبر السلك 4.5A . ما القوة التي تؤثر
على السلك ؟
69-
القوة المؤثرة على سلك متعامد على مجال مغناطيسي منتظم شدته 0.80T تبلغ 3.6N ويبلغ التيار في
السلك 7.5A ما طول السلك ؟
71. The force on a 0.80-m wire that is perpendicular to Earth’s magnetic field is 0.12 N. What is the current in the wire? Use 5.0×10−5 T for Earth’s magnetic field. (Level 1)
71-
تبلغ القوة على سلك طوله 0.80m عمودي على المجال
المغناطيسي للكرة الأرضية 0.12N . ما التيار الذي في السلك ؟استخدم 5.0x10-5Tللمجال المغناطيسي
للكرة الأرضية .
72. Problem Posing Complete this problem so that it must be solved using the concept of magnetic force: “A proton
has a velocity of 600 m/s….” (Level 2)
SOLUTION:
Answers will vary. A possible form of the correct answer would be: “…if it is traveling through a magnetic field of strength 750 mT, what magnetic force does it experience?”
73. A power line carries a 225-A current from east to west, parallel to the surface of Earth. (Level 2)
a. What are the magnitude and direction of the force resulting from Earth’s magnetic field acting on each meter of the wire? Use BEarth = 5.0×10−5 T.
b. In your judgment, would this force be important in designing towers to hold this power line? Explain.
73-
يحمل خط قدرة تياراً يبلغ 225A من الشرق إلى الغرب
بالتوازي مع سطح الكرة الأرضية
.
a-
ما مقدار واتجاه القوة الناتجة عن المجال المغناطيسي للكرة الأرضية والتي تؤثر على
كل متر من السلك ؟ استخدم B=5.0x10-5T للأرض .
b-
في تقديرك : هل ستكون هذه القوة
مهمة في تصميم أبراج تحمل خط القدرة
؟ اشرح ذلك .
74. Galvanometer A galvanometer deflects full-scale for a 50.0-μ A current. (Level 2)
a. What must be the total resistance of the series resistor and the galvanometer to make a voltmeter with 10.0-V full-scale deflection?
b. If the galvanometer has a resistance of 1.0 kΩ, what should be the resistance of the series (multiplier) resistor?
74- الجلفانوميتر : ينحرف مؤشر الجلفانوميتر بمدى كامل مع تيار
يبلغ 50.0µA .
a-
ماذا يجب أن تكون المقاومة الإجمالية للمقاوم التسلسلي والجلفانوميتر لعمل مقياس جهد
كهربائي بانحراف كامل المدى يبلغ 10.0V ؟
b-
إذا كانت مقاومة الجلفانوميتر تبلغ 1.0kΩ ماذا ينبغي أن تكون
مقاومة المقاوم التسلسلي
( متعدد الطبقات )
75. The galvanometer in the previous problem is used to make an ammeter that deflects full-scale for 10 mA. (Level 2)
a. What is the potential difference across the galvanometer (1.0 kΩ resistance) when a current of 50 μA passes through it?
b. What is the equivalent resistance of parallel resistors having the potential difference calculated in a circuit with a total current of 10 mA?
c. What resistor should be placed parallel with the galvanometer to make the resistance calculated in part b?
a. V = IR = (5.00×10−5 A)(1.0×103 Ω) = 0.05 V
76. A beam of electrons moves at right angles to a magnetic field of 6.0×10−2 T. The electrons have a velocity of 2.5×106 m/s. What is the magnitude of the force on each electron? (Level 1)
76-
شعاع من الإلكترونات يتحرك بزواية قائمة على مجال
مغناطيسي يبلغ 6.0x10-2T وتبلغ سرعة
الإلكترونات 2.5x106m/s . ما مقدار القوة على
كل إلكترون ؟
77. A room contains a strong, uniform magnetic field. A loop of fine wire in the room has current in it. The loop is rotated until there is no torque on it as a result of the field. What is the direction of th magnetic field relative to the plane of the coil? (Level 2)
SOLUTION:
The magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of the coil. You would use a right-hand rule to find the direction of the field produced by the coil. The field in the room is in the same direction.
78. Subatomic Particle A muon (a particle with the same charge as an electron but with a mass of 1.88×10−28 kg) is traveling at 4.21×107 m/s at right angles to a magnetic field. The muon experiences a forc of −5.00×10−12 N.
a. How strong is the magnetic field?
b. What acceleration does the muon experience?
78- الجسيم دون الذري
: يتحرك ميون ( جسيم له شحنة
الإلكترون نفسها لكن يكتلة تبلغ 1.88x10-28kg) بسرعة 4.21x107m/s بزواية قائمة على مجال
مغناطيسي يتعرض الجسيم لقوة تبلغ
((-5.00x10-12N
a-
ما قوة المجال المغناطيسي
؟
b –
ما العجلة التي يتعرض لها الميون ؟
79. A force of 5.78×10−16 N acts on an unknown particle traveling at a 90° angle through a magnetic field. If the velocity of the particle is 5.6×104 m/s and the field is 3.20×10−2 T how many elementary charges does the particle carry?
79-
تؤثر قوة تبلغ 5.78x10-16N على جسيم غير معروف
يتحرك بزاوية 900
عبر مجال مغناطيسي . إذا كانت سرعة الجسيم
تبلغ 5.65x104m/s والمجال المغناطيسي
يبلغ 3.20x10-2T . فكم عدد الشحنات
الأولية التي يحملها الجسيم
؟
81. A small bar magnet is hidden in a fixed position inside a tennis ball. Describe an experiment you could do to find the location of the magnet’s poles.
SOLUTION:
Use a compass. The north pole of the compass needle will attract the south pole of the magnet and vice
versa.
82. Compass Suppose you are taking a walk in the woods and realize you are lost. You have a compass, but the red paint marking the north pole of the compass needle has worn off. You also have a length of wire and a flashlight with a battery. How could you identify the north pole of the compass?
SOLUTION:
Connect the wire to the battery so that the current is away from you in one section. Hold the compass
directly above and close to that section of the wire. By a right-hand rule, the end of the compass needle
that points right is the north pole.
83. Two parallel wires carry equal currents
a. If the two currents are in opposite directions, where will the magnetic field from the two wires be larger than the field from either wire alone?
b. Where will the magnetic field from both wires be exactly twice as large as from one wire?
SOLUTION:
a. The magnetic field will be larger anywhere between the two wires.
b. The magnetic field will be twice as large along a line directly between the wires that is equal in
distance from each wire.
84. A nail is attracted to one pole of a permanent magnet. Describe how you could tell whether the metal is magnetized.
SOLUTION:
If not magnetized, either end of the nail would be attracted to either pole of the magnet. If magnetized,
each end of the nail would be attracted to one pole and repelled from the other.
85. Is the magnetic force that Earth exerts on a compass needle less than, equal to, or greater than the force that the needle exerts on Earth? Explain.
SOLUTION:
The strength of the forces are equal according to Newton’s third law.
86. A magnet can attract a piece of iron that is not a permanent magnet. A charged rubber rod can attract an uncharged insulator. What different microscopic processes produce these similar phenomena?
SOLUTION:
The magnet causes the domains in the iron to point in the same direction. The charged rod separates
the positive and negative charges in the insulator.
87. A current-carrying wire runs across a laboratory bench. Describe at least two ways in which you could find the direction of the current.
SOLUTION:
You could use a compass to find the direction of the magnetic field. You could also bring up a strong
magnet and find the direction of the force on the wire, then use a right-hand rule.
88. In which direction, in relation to a magnetic field, would you run a current-carrying wire so that the force on it, resulting from the field, is minimized, or even made to be zero?
SOLUTION:
Run the wire parallel to the magnetic field.
89. A magnetic field can exert a force on a charged particle. Can the field change the particle’s kinetic energy? Explain.
SOLUTION:
No, the force is always perpendicular to the velocity. No work is done. The energy is not changed.
90. As a beam of protons moves from the back to the front of a room, it is deflected upward by a magnetic field. What is the direction of the field?
SOLUTION:
Facing the front of the room, the velocity is forward, the force is upward, and therefore, using a righthand rule, B is to the left.
91. Field lines representing Earth’s magnetic field lines are shown in Figure 32. At what location, poles or equator, is the magnetic field strength greatest? Explain.
SOLUTION:
Earth’s magnetic field strength is greatest at the poles. The field lines are closer together at the poles.
92. A magnetic field of 16 T acts in a
direction due west. An electron is traveling due south at 8.1×105 m/s. What are
the magnitude and direction of the force acting on the electron? (Level 2)
92- يؤثر مجال مغناطيسي بقوة 16T في
اتجاه مستقيم نحو الغرب
.
يتحرك إلكترون في خط مستقيم إلى الجنوب بسرعة 8.1x105m/s . ما مقدار واتجاه القوة المؤثرة على الإلكترون
؟
93. Subatomic Particle A beta particle
(high-speed electron) is traveling at right angles to a 0.60-T magnetic field.
It has a
speed of 2.5×107 m/s. What force acts on the particle? (Level 2)
93- جسيم دون الذري :
يتحرك جسيم بيتا (
إلكترون عالي السرعة
)
بزوايا قائمة على مجال مغناطيسي يبلغ 0.60T . تبلغ سرعته 2.5x107m/s . ما القوة التي تؤثر على الجسيم
؟
SOLUTION:
F = qvB
= (1.6×10−19 C)(2.5×107 m/s)(0.60 T)
= −2.4×10−12 N
94. A copper wire of insignificant
resistance is placed in the center of an air gap between two magnetic poles, as shown in Figure 33. The field is confined to
the gap and has a strength of 1.9 T.
a. Determine the force on the wire
(direction and magnitude) when the switch is open.
b. Determine the force on the wire
(direction and magnitude) when the switch is closed.
c. Determine the force on the wire
(direction and magnitude) when the switch is closed and the battery is
reversed.
d. Determine the force on the wire
(direction and magnitude) when the switch is closed and the wire has two 5.5-Ω
resistors in series.
94- تم وضع سلك نحاسي بمقاومة محدودة في مركز
فجوة هوائية بين قطبين مغناطيسين كما
يظهر في الشكل 33 .
يقتصر المجال على الفجوة وتبلغ قوته 1.9T .
a-حدد القوة المؤثرة على السلك
(
الاتجاه والمقدار
)
عندما يكون المفتاح مفتوحاً
.
b-حدد القوة المؤثرة على السلك
(
الاتجاه والمقدار
) عند
إغلاق المفتاح.
C- حدد القوة المؤثرة على السلك
(
الاتجاه والمقدار
) عند
إغلاق المفتاح وعكس البطارية
D- حدد القوة المؤثرة على السلك
(
الاتجاه والمقدار
) عند
إغلاق المفتاح ووجود مقاومين اثنين يبلغان 5.5Ω على
السلك بالتسلسل
.
a. 0 N. With no current, no magnetic field is produced by the wire. Copper is not a
magnetic material
c. Down, 0.62 N. The direction of the force is given by a right-hand rule, and the magnitude of the force is the same as in part b.
d. Up, 0.31 N. The direction of the force is given by a right-hand rule.
95. Two galvanometers are available. One
has 50.0-μ
A full-scale sensitivity and the other has 500.0-μ A full-scale
sensitivity.
Both have the same coil resistance of 855 Ω. Your challenge is to convert them
to measure a current of
100.0 mA,
full-scale. (Level 2)
a. Determine the shunt resistor for
the 50.0-μA
meter.
b. Determine the shunt resistor for
the 500.0-μA
meter.
c. Determine which of the two is
better for actual use. Explain.
95-يتوفر جلفانوميتران . تبلغ
حساسية أحدهما 50.0µA بمدى
كامل وتبلغ حساسية الآخر 500.0µA بمدى
كامل
.
كلاهما له مقاومة الملف نفسها والتي تبلغ 855Ω
يتمثل التحدي الذي أمامك في تحويلهما لقياس شدة
تيار تبلغ 100.0mA بمدى
كامل
.
a - حدد مقاوم مجزيء
التيار الكهربائي للمقياس 50.0µA ..
b-حدد مقاوم مجزيء التيار الكهربائي للمقياس 500.0µA
C- حدد أيهما أفضل في الاستخدام الفعلي اشرح
ذلك .
a. Find the voltage across the meter coil at full scale.
V = IR = (50.0 μ A)(855 Ω) = 0.0428 V
Calculate the shunt resistor.
b. Find the voltage across the meter coil at full scale.
V = IR = (500.0 μ A)(855 Ω) = 0.428 V Calculate the shunt resistor.
c. The 50.0-μ A meter is better. Its lower shunt resistance will do less to alter the total resistance of the circuit being measured. An ideal ammeter has 0-Ω resistance.
96. Loudspeaker The magnetic field in a
loudspeaker is 0.15 T. The wire makes 250 turns around a cylindrical form that
is 2.5 cm in diameter. The resistance of the wire is 8.0 Ω. Find the force on
the wire when 15 V is placed across the wire. (Level 2)
96- مكبر الصوت : يبلغ المجال المغناطيسي في مكبر صوت 0.15T . يدور
السلك المكون من
250 لفة حول شكل اسطواني يبلغ قطره 2.5cm . تبلغ
مقاومة السلك 8.0ῼ . أوجد القوة المؤثرة على السلك عند وضع 15V عبر السلك
.
97. A wire carrying 15 A of current has a
length of 25 cm in a uniform magnetic field of 0.85 T. Using the equation F
= ILB(sin θ ), find the force on the wire when it makes the following angles
with the magnetic field lines.(Level 2)
97- سلك
يحمل تياراً شدته 15A بطول
25Cm في
مجال مغناطيسي منتظم يبلغ 0.85T . باستخدم
المعادلة F=ILBsinѳ أوجد القوة المؤثرة على السلك عندما
يصنع الزوايا التالية مع خطوط المجال المغناطيسي
SOLUTION:
a. F = ILB(sin θ)
= (15 A)(0.25 m)(0.85 T)(sin 90°)
= 3.2 N
b. F = ILB(sin θ )
= (15 A)(0.25 m)(0.85 T)(sin 45°)
= 2.3 N
c. sin 0° = 0
so F = 0 N
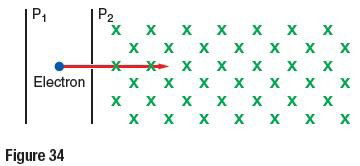
98. An electron is accelerated from rest
through a potential difference of 2.0×104 V, which exists between plates P1
and P2,
shown in Figure
34. The electron then passes through a small opening into a magnetic field of
uniform field
strength. As
indicated, the magnetic field is directed into the page. (Level 2)
a. State the direction of the
electric field between the plates as either P1 to P2 or P2 to P1.
b. In terms of the information
given, calculate the electron’s speed at plate P2.
c. Describe the motion of the
electron through the magnetic field.
98- يتسارع إلكترون من السكون حتى فرق جهد
يبلغ 2.0x104V والذي يوجد بين السطحين P1 و P2
الظاهرين في الشكل 34
. ثم
يمر الإلكترون عبر فتحة صغيرة إلى مجال مغناطيسي
منتظم يتجه كما يظهر إلى داخل الصفحة .
a-حدد اتجاه المجال الكهربائي بين السطحين
إما P1 إلى P2 أو P2 إلى P1.
-bمن حيث المعلومات المذكورة احسب سرعة
الإلكترون عند السطح P2 .
C-صف حركة الإلكترون عبر المجال المغناطيسي
.
SOLUTION:
a. from P2 to P1
99. Synchrotron The LHC synchrotron has a 27-km circumference and 1232 bending magnets. Protons of mass 1.67×10–27 kg and charge 1.602×10–19 C are all traveling at speeds close to the speed of light, 3.00×108 m/s. What
magnetic field would be required to bend their paths into a circle? Hint: Recall that centripetal force is given by F = mv 2/r. The forces come from the particle moving through the magnetic field. The radius of a circle of circumference C is r = C/2π. Note that due to the effects of special relativity on the protons, the actual magnetic
field needed is 8.36 T.
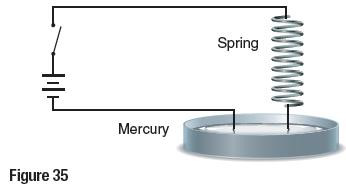
100. Apply Concepts A current is sent through a vertical spring, as shown in Figure 35. The end of the spring is in a cup filled with mercury. What will happen? Why?
SOLUTION:
When the current passes through the coil, the magnetic field increases and forces cause the spring to compress. The wire comes out of the mercury, the circuit opens, the magnetic field decreases, and the spring drops down. The spring will oscillate up and down.
101. Reverse Problem Write a physics problem with real-life objects for which the following equation would be part of the solution:
SOLUTION:
Answers will vary, but a correct form of the answer is: “A proton moves through a magnetic field of 2.3 T. If it is to experience a force of magnitude 60 N, how fast must it be moving?”
102. Apply Concepts The magnetic field produced by a long, current-carrying wire is represented by B = (2×10−7 T · m/A)(I/d ), where B is the field strength in teslas, I is the current in amps, and d is the distance from the wire in meters. Use this equation to estimate the magnetic fields in the following scenarios.
a. The wires in your home seldom carry more than 10 A. How does the magnetic field that is 0.5 m from such a wire compare to Earth’s magnetic field?
b. High-voltage power transmission lines often carry 200 A at potential differences as high as 765 kV. Estimate the magnetic field on the ground under such a line, assuming that it is about 20 m high. Ho does this field compare with a magnetic field in your home?
This is half as strong as the field in part a.
















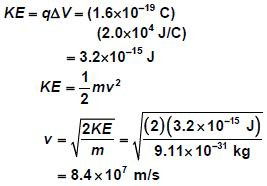




وين سوال 94
ردحذفجزاك الله خير
ردحذفشكرا ما قصرتون :)
ردحذفولكن ايت سؤال 26
حذفالسلام عليكم و رحمة الله و بركاته
ردحذفالله يجزيكي ألف خير يأ أبلة
أعتمد على شرحك من صف تاسع و لو أني أدرس بالانجليزي
و الحمدلله اتحسن مستواي
ان شاء الله اكمل معك حتى صف 12
السلام عليكم
ردحذفلوسمحتي معلمة الأسئلة من س94 إلى 98 لا يوجد لها روابط و بحثت عن الفيديوهات في القناه غير موجودة