الوحدة 24 الاهتزازات والموجات
بوربونت دروس القسم 1 الحركة الدورية
https://drive.google.com/file/d/150jqgEQ_xhFr_FvWgT2WGVT3I8bMvLT7/view?usp=sharing
درس القسم 2 خصائص الموجات
https://youtu.be/syFAVtvKTTo
درس القسم 2 خصائص الموجات
https://youtu.be/syFAVtvKTTo
بور بونت درس القسم 2 خصائص الموجات
بور بونت القسم 3 سلوك الموجات
اسئلة ومسائل باللغة الانجليزية مع الحلول
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B976YZX4SobqaGNrWS1DSmotczA/view?usp=sharing
الاختبار المعياري في الاهتزازات والموجات
https://youtu.be/RrDBhMDALME
رابط مدونة الاهتزازات والموجات
https://draft.blogger.com/blog/page/edit/3599613972949345658/8266414410123097713
حل المسائل
.78- تنشأ موجات مستقرة في الأوتار الأربعة الموضّحة في
حل المسائل
1- ما مقدار ثابت نابض يستطيل بمقدار 12cm عندما يُعلق به جسم يزن 24N ؟
2- يضغط نابض ثابته k=144N.m بمقدار 16.5cm كم تبلغ طاقة الوضع
المر ونية للنابض ؟
3- إذا كان ثابت نابض 56N/m ما مقدار استطالته عندما تُعلق كتلة تزن 18N من طرفه ؟
4- تحفيز: نابض ثابته 256N/m ما مقدار المسافة
التي يجب أن يستطيلها ليختزن طاقة وضع مرونية تساوي 48J
5-
ما مقدار الزمن الدوري لبندول يبلغ طوله 1.0m؟
6-
ما الطول المناسب لبندول على سطح القمر عندما يكون g=1.6N/Kg حتى يكون زمنه الدوري 2.0S؟
7- تحفيز: إذا كان الزمن الدوري لبندول طوله 0.75m يساوي 1.8s على أحد الكواكب فما
مقدار g لهذا الكوكب ؟
اسئلة اتقان المفاهيم من 8-----14
مسألة تحدي الفيزياء
15 . يُسمع صوت الموجة
الصوتية الذي تصدره دقات الساعة على بُعد515m بعد مرور
1.50s بناءً على هذه القياسات،
- ما سرعة الصوت في الهواء؟ -a
) فكم
يبلغ الزمن الدوري لهذه الموجة؟ 436Hz) - يبلغ تردد الموجة الصوتية-b
C-ما طول موجة صوت دقات الساعة؟
16. إذا كنت تريد زيادة أطوال الموجات في الحبل، فهل
ينبغي أن تهزّه بأعلى تردد أم بأقل تردد؟
17-
كم تبلغ سرعة الموجة الدورية التي يبلغ ترددها 3.50Hz وطولها الموجي
0.700m
18 . كيف تؤثر زيادة طول
الموجة بنسبة % 50 في تردد موجة على حبل؟
19. تبلغ سرعة موجة
مستعرضة في وتر15.0m/s إذا أحدث المصدر
اهتزازا
يبلغ تردد6.00Hz فكم يبلغ طول موجته .
20-
تنشأ خمسة أطوال موجية كل 0.100S في خزان ماء . كم تبلغ سرعة الموجة
إذا كان طول الموجة السطحية 1.20cm ؟
21- تنتقل موجة طولية
دورية يبلغ ترددها 20.0Hz . على طول زنبرك حلزوني
في لعبة . إذا كانت المسافة بين الانضغاطات المتتالية 0.600m فكم تبلغ سرعة الموجة؟
22-
كيف يتغير تردد الموجة عندما يتضاغف زمنها الدوري ؟
23-
وضح التغير الذي يطرأ على طول الموجة عندما يقل زمنها الدوري إلى نصف ما كان عليه .
24-
إذا زادت سرعة الموجة بمقدار 15
مرة على سرعتها الأصلية وظل التردد ثابتاً .
فما التغير الذي يطرأ على طولها الموجي
؟
25- تحفيز :
أصدر شخص صراخاً باتجاه منحدر رأسي كما هو موضح في الشكل 12 فسمع صدى الصوت بعد
مرور 2.75S .
a-
فما سرعة صوت هذا الشخص في الهواء
؟
b –
يبلغ طول موجة الصوت 0.750m فما تردده ؟
C-
ما الزمن الدوري للموجة
؟
26- الفكرة الرئيسة : لنفترض أنه طُلب منك وزميلك في المختبر توضيح أن الموجة
المستعرضة تنقل الطاقة من دون نقل المادة .
كيف يمكنكما فعل ذلك؟
27- خصائص الموجة : إذا أردت إحداث
موجات مستعرضة على حبل عن طريق هز يدك من طرف إلى آخر . وبدأت بهز الحبل أسرع من دون تغيير المسافة التي تتحرك فيها يدك. ماذا يحدث لسعة
الموجة وطول الموجة والتردد والزمن الدوري والسرعة المتجهة ؟
28- الموجات الطولية : صف الموجات الطولية . ما أنواع الأوساط
التي تنتقل من خلالها الموجات الطولية
؟
https://youtu.be/c03n964b3nI
اتقان المفاهيم
36-37-38-39-40-41-42-43-51-52-53-54-55-56-57-58-59-60
https://youtu.be/dHOopDhDtNY
اتقان المفاهيم
36-37-38-39-40-41-42-43-51-52-53-54-55-56-57-58-59-60
https://youtu.be/dHOopDhDtNY
33. Refraction of Waves In Figure 20, the wave changes direction as it passes from one medium to another. Can
two-dimensional waves cross a boundary between two mediums without changing direction? Explain.
SOLUTION:
yes, if they strike the boundary while traveling normal to its surface, or if they have the same speed in both media
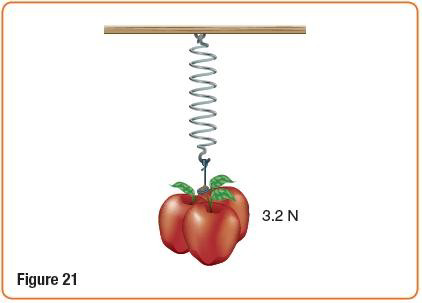
44. A spring stretches 0.12 m when some apples are suspended from it, as shown in Figure 21. What is the spring constant of the spring? (Level 1)
44 – إذا استطال نابض مسافة 0.12m عندما عُلق في أسفله عدد من التفاحات وزنها 3.2N كما في الشكل 21 فما مقدار ثابت النابض ؟
45. Car Shocks Each of the coil springs of a car has a spring constant of 25,000 N/m. How much is each spring compressed if it supports one-fourth of the car’s 12,000-N weight? (Level 1)
45 – صدمات السيارات : تتضمن كل النوابض اللولبية لسيارة ثابت
مرونة يبلغ 25.000N/m ما مقدار انضغاط كل
نابض عندما يحمل ربع سيارة وزنها 12,000N؟
46 –
يستطيل نابض يبلغ ثابته 27N/m لمسافة مقدارها 16cm كم تبلغ طاقة الوضع المرونية للنابض ؟
47. Rocket Launcher A toy rocket launcher contains a spring with a spring constant of 35 N/m. How far must the spring be compressed to store 1.5 J of energy? (Level 2)
47 – قاذفة الصواريخ : تتضمن لعبة قاذفة
الصواريخ نابضاً يبلغ ثابته 35N/m ما المسافة التي يجب
أن يتضمنها النابض لتخزين 15J من الطاقة ؟
48. Force magnitude-versus-length data for a spring are plotted on the graph in Figure 22. (Level 3)
a. What is the spring constant of the spring?
b. What is the energy stored in the spring when it is stretched to a length of 0.50 m?
48-
مثلت بيانات مقدار القوة والاستطالة لنابض في الرسم البياني الوارد في الشكل 22
a- أوجد ثابت النابض ؟
b-
أوجد طاقة الوضع المرونية للنابض عندما يستطيل 0.50m
49. How long must a pendulum be to have a period of 2.3 s on the Moon, where g = 1.6 N/kg? (Level 3)
49-
ما مقدار الطول اللازم للبندزل ليصبح زمنه الدوري 2.3s على سطح القمر إذا
كانت g=1.6N/kg
50. Ranking Task Rank the following pendula according to period, from least to greatest. Specifically indicate any
ties. (Level 3)
A: 10 cm long, mass 0.25 kg
B: 10 cm long, mass 0.35 kg
C: 20 cm long, mass 0.25 kg
D: 20 cm long, mass 0.35 kg
50- مهمة الترتيب : رتب البندولات التالية وفقاً للزمن
الدوري من الأصغر إلى الأكبر
.
A-
الطول 10cm والكتلة 0.25kg
B-
الطول 10cm والكتلة 0.25kg
C-
الطول 20cm والكتلة 0.35kg
D-
الطول 20cm والكتلة 0.35kg
https://youtu.be/fpcATDVZWcc
51. Explain how the process of energy transfer associated with throwing a ball is different from the process of energy
transfer associated with a mechanical wave.
SOLUTION:
When throwing a ball, matter (in the ball) is transferred from one place to another. In a mechanical
wave, energy transfers without matter traveling from place to place.
52. What are the differences among transverse, longitudinal, and surface waves?
SOLUTION:
A transverse wave causes the particles of the medium to vibrate in a direction that is perpendicular to the direction in which the wave is moving. A longitudinal wave causes the particles of the medium to
vibrate in a direction parallel with the direction of the wave. Surface waves have characteristics of both.
53. Waves are sent along a spring of fixed length.
a. Can the speed of the waves in the spring be changed? Explain.
b. Can the frequency of a wave in the spring be changed? Explain.
SOLUTION:
a. Speed of the waves depends only on the medium and cannot be changed.
b. Frequency can be changed by changing the rate at which the waves are generated.
54. What is the wavelength of a wave?
SOLUTION:
Wavelength is the distance between two adjacent points on a wave that are in phase.
55. Suppose you send a pulse along a rope. How does the position of a point on the rope before the pulse arrives
compare to the point’s position after the pulse has passed?
SOLUTION:
Once the pulse has passed, the point is exactly as it was prior to the pulse reaching the point.
56. What is the difference between a wave pulse and a periodic wave?
SOLUTION:
A pulse is a single disturbance in a medium, whereas a periodic wave consists of several adjacent
disturbances.
57. Describe the difference between wave frequency and wave velocity.
SOLUTION:
Frequency is the number of vibrations per second of a part of the medium. Velocity describes the motion of the wave through the medium.
58. Suppose you produce a transverse wave by shaking one end of a spring from side to side. How does the frequency of your hand compare with the frequency of the wave?
SOLUTION:
They are the same.
59. When are points on a wave in phase with each other? When are they out of phase? Give an example of each.
SOLUTION:
Points are in phase when they have the same displacement and the same velocity. Otherwise, the points are out of phase. Two crests are in phase with each other. A crest and a trough are out of phase with
each other.
60. Describe the relationship between the amplitude of a wave and the energy it carries.
SOLUTION:
The energy carried by a wave is proportional to the square of its amplitude.
61. Building Motion The Willis Tower in Chicago sways back and forth in the wind with a frequency of about 0.12 Hz. What is its period of vibration? (Level 1)
61 . حركة
بناية : يتأرجح برج ويلبيس في
شيكاغو ذهاباً وإياباً في مهب الريح بتردد
0.12Hz تقريباً . كم يبلغ الزمن الدوري
للاهتزاز؟
62. Ocean Waves An ocean wave has a length of 12.0 m. A wave passes a fixed location every 3.0 s. What is the
speed of the wave? (Level 1)
62 . موجات
المحيط: يبلغ طول موجة محيط 12.0m وتمر موجة بموقع ثابت
كل 3.0s كم تبلغ سرعة الموجة ؟
63. The wavelength of water waves in a shallow dish is 6.0 cm. The water moves up and down at a rate of
4.8 oscillations/s. (Level 1)
a. What is the speed of the waves?
b. What is the period of the waves?
63 . يبلغ طول الموجة لموجات الماء في طبق مسطح 6.0cm يتحرك الماء صعوداً
وهبوطاً بمعدل 4.8 ترددات في الثانية .
a-
كم تبلغ سرعة الموجات ؟
b –
كم يبلغ الزمن الدوري لهذه الموجات
؟
64. Water waves in a lake travel 3.4 m in 1.8 s. The period of oscillation is 1.1 s. (Level 1)
a. What is the speed of the water waves?
b. What is their wavelength?
64 . تنتقل موجات الماء في بحيرة بمعدل 3.4m خلال 1.8s يبلغ الزمن الدوري
للذبذبة 1.1s
a-
كم تبلغ سرعة موجات الماء ؟
b –
كم يبلغ طول موجتها ؟
65. Sonar A sonar signal of frequency 1.00 ×106 Hz has a wavelength of 1.50 mm in water. (Level 2)
a. What is the speed of the signal in water?
b. What is its period in water?
65 السونار : يبلغ طول موجة إشارة
سونار 1.50mm وترددها 1.00x106Hz في الماء
a-
كم تبلغ سرعة الاشارة في الماء ؟
b –
كم يبلغ الزمن الدوري لها في الماء؟
66. The speed of sound in water is 1498 m/s. A sonar signal is sent straight down from a ship at a point just below the water surface, and 1.80 s later the reflected signal is detected. How deep is the water? (Level 2)
66
تبلغ سرعة الصوت في الماء 1498m/s تُرسل إشارة سونار من
سفينة مباشرة إلى أسفل عند نقطة تحت سطح الماء مباشرة وكُشفت الإشارة المنعكسة بعد
مرور 1.80s كم يبلغ عمق الماء ؟
67. A sound wave of wavelength 0.60 m and a velocity of 330 m/s is produced for 0.50 s. (Level 2)
a. What is the frequency of the wave?
b. How many complete waves are emitted in this time interval?
c. After 0.50 s, how far is the front of the wave from the source of the sound?
67
–تحدث موجة صوتية طول موجتها 0.60m وسرعتها 330m/s خلال 0.50s
A-
ما تردد الموجة ؟
B-
كم عدد الموجات الكاملة المرسلة في هذه الفترة الزمنية ؟
C-
بعد مرور 0.50s كم تبعد مقدمة الموجة
عن مصدر الصوت ؟
68. Pepe and Alfredo are resting on an offshore platform after a swim. They estimate that 3.0 m separates a trough
and an adjacent crest of each surface wave on the lake. They count 12 crests in 20.0 s. Calculate how fast the
waves are moving. (Level 3)
68
–يستريح مازن وعبدالله على منصة بحرية بعد السباحة . قدر كلاهما أن
المسافة التي تفصل بين القاع والقمة المجاورة لكل موجة سطحية في البحيرة 3.0m عد كلاهما 12 قمة خلال 20.0s احسب مقدار السرعة
التي تنتقل بها الموجات .
69. Earthquakes The velocity of the transverse waves produced by an earthquake is 8.9 km/s, and that of the
longitudinal waves is 5.1 km/s. A seismograph records the arrival of the transverse waves 68 s before the arrival of
the longitudinal waves. How far away is the earthquake? (Level 3)
69 –الزلازل : تبلغ السرعة للموجات
المستعرضة التي يحدثها زلزال 8.9km/s وتبلغ السرعة للموجات الطولية 5.1km/s يسجل جهاز قياس الزلازل وصول الموجات المستعرضة قبل الموجات
الطولية بمقدار 68S . ما مقدار المسافة
التي يبعدها الزلزال؟
اتقان المفاهيم
70,71,72,73,74,75,76,,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,8670. When a wave crosses a boundary between a thin rope and a thick rope, as shown in Figure 23, its wavelength and speed change, but its frequency does not. Explain why the frequency is constant.
SOLUTION:
The frequency depends only on the rate at which the thin rope is shaken and the thin rope causes the vibrations in the thick rope.
71. How does a wave pulse reflected from a rigid wall differ from the incident pulse?
SOLUTION:
The reflected pulse will be inverted.
72. Describe the motion of the particles of a medium located at the nodes of a standing wave.
SOLUTION:
Nothing, the medium does not move.
73. Standing Waves A metal plate is held fixed in the center and sprinkled with sugar. With a violin bow, the plate is
stroked along one edge and made to vibrate. The sugar begins to collect in certain areas and move away from
others. Describe these regions in terms of standing waves.
SOLUTION:
Bare areas are antinodal regions where there is maximum vibration. Sugar-covered areas are nodal
regions where there is no vibration.
74. If a string is vibrating in four parts, there are points where it can be touched without disturbing its motion. Explain.
How many of these points exist?
SOLUTION:
A standing wave exists and the string can be touched at any of its five nodal points.
75. Wavefronts pass at an angle from one medium into a second medium, where they travel with a different speed.
Describe two changes in the wavefronts. What does not change?
SOLUTION:
The wavelength and direction of the wavefronts change. The frequency does not change.
77. Guitars The wave speed in a guitar string is 265 m/s. The length of the string is 63 cm. You pluck the center of
the string by pulling it up and letting go. Pulses move in both directions and are reflected off the ends of the string.
a. How long does it take for the pulse to move to the string end and return to the center?
b. When the pulses return, is the string above or below its resting location?
c. If you plucked the string 15 cm from one end of the string, where would the two pulses meet?
77. أجهزة الجيتار تبلغ
سرعة الموجة في وتر الجيتار265 m/s ويبلغ طول الوتر 63cm وعندما
حُرِّك منتصف الوتر بسحبه إلى أعلى وتركه، انتقلت الموجات في كلا
الاتجاهين وانعكست بعيدًا من طرفي الوتر.
-a ما
المدة الزمنية التي تستغرقها الموجه لتنتقل عبرالوتر وتعود إلى المنتصف؟
b -عندما
تعود الموجات، هل يوجد الوتر فوق موقعه المستقر أم أسفله؟
-c- إذا
حرّكتَ الوتر مسافة 15cm
من أحد طرفيه، فأين
ستلتقي النبضتان؟
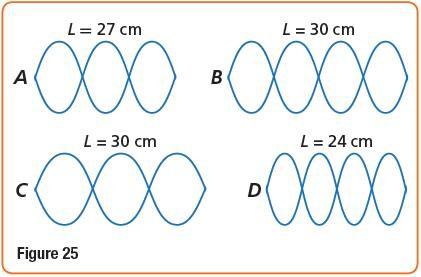
78. Standing waves are created in the four strings shown in Figure 25. All strings have the same mass per unit length and are under the same tension. The lengths of the strings, L, are given. Rank the frequencies of the oscillations,
from largest to smallest. (Level 2)
.78- تنشأ موجات مستقرة في الأوتار الأربعة الموضّحة في
الشكل 25. إنّ كتلة كل الأوتار
هي نفسها لكل وحدة طول
وتتأثر جميعها بقوة الشد نفسها. إذا كانت أطوال الأوتار (L) معلومة . رتب ترددات الموجات
من الأكبر إلى الأصغر
88. Radio Wave AM-radio signals are broadcast at frequencies between 550 kHz (kilohertz) and 1600 kHz and travel
3.0×108 m/s. (Level 1)
a. What is the range of wavelengths for these signals?
b. FM frequencies range between 88 MHz (megahertz) and 108 MHz and travel at the same speed. What is the range of FM wavelengths?
89-إذا
كان الزمن اللازم لتغيير موجة الماء من مستوى الاتزان إلى القمة 0.18s . احسب:
-a طول الموجة(التصحيح ما المسافة المقطوعة في هذا الزمن )
b -الزمن
الدوري للموجة c-تردد
الموجة
https://youtu.be/JayrNmThOgo
90. When a 225-g mass is hung from a spring, the spring stretches 9.4 cm. The spring and mass then are pulled 8.0 cm from this new equilibrium position and released. Find the spring constant of the spring. (Level 2)
90. عند تعليق كتلة كتلتها 225 g من زنبرك، يمتد الزنبرك مسافة 9.4 cm. ثم يتم سحب الزنبرك والكتلة بمقدار 8.0 cm
من هذا الموقف التوازن الجديد وأطلق سراحه. أوجد ثابت الزنبرك. (المستوي 2)
91. You are floating offshore at the beach. Even though the waves are steadily moving toward the beach, you don’t
move much closer to the beach. (Level 2)
a. What type of wave are you experiencing as you float in the water?
b. Explain why the wave does not move you closer to shore.
c. In the course of 15 s you count ten waves that pass you. What is the period of the waves?
d. What is the frequency of the waves?
e. You estimate that the wave crests are 3 m apart. What is the velocity of the waves?
f. After returning to the beach, you learn that the waves are moving at 1.8 m/s. What is the actual wavelength of the waves?
a. surface waves
b. The displacement is perpendicular to the direction of the wave—in this case, up and down.
93. You have a mechanical fish scale that is made with a spring that compresses when weight is added to a hook attached below the scale. Unfortunately, the calibrations have completely worn off the scale. However, you have
one known mass of 500.0 g that compresses the spring 2.0 cm. (Level 2)
a. What is the spring constant for the spring?
b. If a fish displaces the spring 4.5 cm, what is the mass of the fish?
93. لديك ميزان سمك ميكانيكي مصنوع من زنبرك ينضغط عند إضافة الوزن إلى الخطاف
مرفقة أسفل المقياس. لسوء الحظ، فقد تآكلت المعايرات تمامًا. ومع ذلك، لديك
كتلة معروفة كتلتها 500.0 g تضغط الزنبرك بمقدار 2.0 cm. (المستوي 2)
أ. ما هو ثابت الربيع لفصل الربيع؟
ب. إذا أزاحت سمكة الزنبرك مسافة 4.5 سم، فما كتلة السمكة؟
94. Bridge Swinging In the summer over the New River in West Virginia, several teens swing from bridges with
ropes, then drop into the river after a few swings back and forth. (Level 2)
a. If Pam is using a 10.0-m length of rope, how long will it take her to complete one full swing?
b. If Mike has a mass that is 20 kg more than Pam’s, how would you expect the period of his swing to differ from
Pam’s?
c. At what point in the swing is KE at a maximum?
d. At what point in the swing is PE at a maximum?
e. At what point in the swing is KE at a minimum?
f. At what point in the swing is PE at a minimum?
SOLUTION:
a.
b. There should be no difference. T is not affected by mass.
c. At the bottom of the swing, KE is at a maximum.
d. At the top of the swing, PE is at a maximum.
e. At the top of the swing, KE is at a minimum.
f. At the bottom of the swing, PE is at a minimum.
95. Car Springs When you add a 45-kg load to the trunk of a new small car, the two rear springs compress an additional 1.0 cm. (Level 2)
a. What is the spring constant for each of the springs?
b. What is the increase in each of the spring’s potential energy after loading the trunk?
96. Amusement Ride You notice that your favorite amusement-park ride seems bigger. The ride consists of a carriage that is attached to a structure so it swings like a pendulum. You remember that the carriage used to swing from one position to another and back again eight times in exactly 1 min. Now it only swings six times in 1 min. Give your answers to the following questions to two significant digits.
a. What was the original period of the ride?
b. What is the new period of the ride?
c. What is the new frequency?
d. How much longer is the arm supporting the carriage on the larger ride?
e. If the park owners wanted to double the period of the ride, what percentage increase would need to be made to the length of the pendulum?
.
e - Because of the square relationship, there would need to be a 4 times increase in the length of the
pendulum, or a 300% increase.












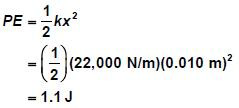




ممكن مسألة 89
ردحذفالمسألة سهلة فقط هناك خطأ في ترجمة الطلب الأول وهوما المسافة المقطوعة خلال الزمن المذكور وفقك الله
حذفشكرا
حذفأزال المؤلف هذا التعليق.
ردحذفممكن سؤال 77
ردحذفممكن 90/93/94
ردحذفممكن مسألة 88 وشكرا جزيلا
ردحذفممن سؤال 97 صفحة 141 للصف العاشر؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟
ردحذف